I've been looking at documentation on Resource Management over the last few days. Here are some of the articles that I have found. Unfortunately, much of the information I found is based on the Solaris 9 and even Solaris 8 implementations of Resource Manager, which is only somewhat useful when looking at Solaris 10.
If you are aware of additional resources, please feel free to add them to the comments on this post.
Here are the best items I've found:
System Administration Guide: Solaris Containers-Resource Management and Solaris Zones from the Solaris 10 documentation. This is quite well-written, though organized differently than I would have done it.
The Sun BluePrints Guide to Solaris Containers by Foxwell, Lageman, Hoogeveen, Rozenfeld, Setty and Victor. The Resource Management section is also quite well-written, and I found the organization to be more helpful than the manual in the Solaris 10 docs.
Solaris Resource Management by Galvin in SysAdmin. This is a high-level introduction. Though it is specific to Solaris 9, it is still the best quick introduction to the subject I've come across.
Capping a Solaris processes memory by matty is a blog page describing the ability of Solaris 10 to use rcapd to manage memory. This is a brief but thorough discussion of this topic.
Labels
- news (101)
- Linux (72)
- tips (36)
- ubuntu (32)
- hardware (24)
- videos (24)
- howtos (21)
- kde (20)
- open source (20)
- solaris (18)
- solaris interview questions (18)
- external links (10)
- fedora (10)
- windows (10)
- debian (8)
- kernel (8)
- solaris interview questions and answers (8)
- MCSE Videos (6)
- commands (6)
- sun (6)
- linus torvalds (5)
- Sun Solaris 10 CBT (4)
- network administration (4)
- web design (4)
- solaris-express (3)
- backup (2)
- virtualization (1)
Resource Management resources
FizzBall - A well designed enjoyable game for Linux
- Which baby animal can be called a kid? Goat
- A group of these animals can be called a Mob. - I forgot the answer ;-)
- A group of these animals can be called a pride. Lions
- Which baby animal can be called a gosling ? Goose
- Which animal's baby can be called a snakelet ? snake
- A group of these animals can be called a Parliament. Owl
FizzBall game features
- Over 180 unique levels of game play.
- The game stage is automatically saved once you exit the game and you can continue where you left off the next time you start playing.
- Multiple users can be created and each user's game is saved separately.
- There are two modes - Regular mode and Kids mode. The kids mode does not allow you to lose the balls and includes fun quizzes between levels.
- If you lose all your bubbles, you can still continue with the game, though all your scores will be canceled.
- Get trophys for achieving unique feats. For example, I recieved a trophy for capturing an alien without getting hit by a laser :-) .
Pros of the game
- Eye catching design and excellent graphics.
- Is educative for little kids as well as entertaining for all ages.
- Over 180 levels in both the regular and kids mode of the game.
Is not released under GPL, with the full version of the game costing USD $19.95. A time limited demo version of the game is available though for trying out before buying. But having played the full game, I would say that the money is well spent.
The good news is, professional game developers are seriously eyeing the Linux OS alongside Windows as a viable platform to release their games, FizzBall being a case to the point.
Labels: games
Introduction
This blog is designed to be a companion to my Solaris Troubleshooting web site, hosted by Princeton University.
I used to have an email link to solicit feedback on the web site. I received some outstanding feedback, but I also received an outstanding amount of spam.
I am in the process of updating the site to include more Solaris 10 specific information, especially with regards to Resource Management and dtrace. I've posted a first cut at a Resource Management page.
Thanks to everyone who contributed to the old Solaris 8 site, and a special thanks to Princeton University for continuing to host the site long after I no longer worked on their Unix team.
--Scott Cromar
Richard M Stallman talks on GPL version 3 at the 5th International GPLv3 Conference in Japan
Labels: Richard Stallman
Making the right decisions while buying a PC
The gist of his choice filters down to the following:
- ATX tower case - is capable of holding a full size motherboard with space for several optical drives and is ideal for home users and gaming enthusiasts.
- CPU - As of now Intel core duo provides the best power-performance-price ratio. Enough applications have been optimized for dual-core chips that these should be considered for any moderate to heavy use, especially when multitasking.
- Always go for motherboards that have the PCI Express slots over the now fast becoming outdated ordinary PCI slots.
- And with respect to memory (RAM), your best bet is to go for atleast DDR-400 and above though ideally DDR2-800 is recommended. And don't even think of a machine with less than 512 MB RAM. The article strongly recommends a choice of 2 GB memory if you can afford it as near future applications and OSes will demand that much memory.
- On the storage front, if you are in the habit of archiving video or hoarding music on your hard disk, do consider atleast a hard disk of 150 GB. The article recommends Western Digital's Raptor 150 GB drives if you are on the look out for better performance and Seagate Barracuda 750 GB for those on the look out for larger capacity drives. Both are costly though.
- And do go for a DVD writer over a CD-RW/DVD combo.
Labels: hardware
A peep into how Compact Discs are manufactured
Update (Feb 14th 2007): The Youtube video clip embedded here has been removed as I have been notified by its real owners that the video clip is copyrighted.
Ifconfig - dissected and demystified
# ifconfig eth0 192.168.0.1 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.0.255 up
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:70:40:42:8A:60
inet addr:192.168.0.1 Bcast:192.168.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
UP BROADCAST NOTRAILERS RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:160889 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:22345 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:33172704 (31.6 MiB) TX bytes:2709641 (2.5 MiB)
Interrupt:9 Base address:0xfc00
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:16436 Metric:1
RX packets:43 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:43 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
RX bytes:3176 (3.1 KiB) TX bytes:3176 (3.1 KiB)
- Link encap:Ethernet - This denotes that the interface is an ethernet related device.
- HWaddr 00:70:40:42:8A:60 - This is the hardware address or MAC address which is unique to each ethernet card which is manufactured. Usually, the first half part of this address will contain the manufacturer code which is common for all the ethernet cards manufactured by the same manufacturer and the rest will denote the device Id which should not be the same for any two devices manufactured at the same place.
- inet addr - indicates the machine IP address
- Bcast - denotes the broadcast address
- Mask - is the network mask which we passed using the netmask option (see above).
- UP - This flag indicates that the kernel modules related to the ethernet interface has been loaded.
- BROADCAST - Denotes that the ethernet device supports broadcasting - a necessary characteristic to obtain IP address via DHCP.
- NOTRAILERS - indicate that trailer encapsulation is disabled. Linux usually ignore trailer encapsulation so this value has no effect at all.
- RUNNING - The interface is ready to accept data.
- MULTICAST - This indicates that the ethernet interface supports multicasting. Multicasting can be best understood by relating to a radio station. Multiple devices can capture the same signal from the radio station but if and only if they tune to a particular frequency. Multicast allows a source to send a packet(s) to multiple machines as long as the machines are watching out for that packet.
- MTU - short form for Maximum Transmission Unit is the size of each packet received by the ethernet card. The value of MTU for all ethernet devices by default is set to 1500. Though you can change the value by passing the necessary option to the ifconfig command. Setting this to a higher value could hazard packet fragmentation or buffer overflows. Do compare the MTU value of your ethernet device and the loopback device and see if they are same or different. Usually, the loopback device will have a larger packet length.
- Metric - This option can take a value of 0,1,2,3... with the lower the value the more leverage it has. The value of this property decides the priority of the device. This parameter has significance only while routing packets. For example, if you have two ethernet cards and you want to forcibly make your machine use one card over the other in sending the data. Then you can set the Metric value of the ethernet card which you favor lower than that of the other ethernet card. I am told that in Linux, setting this value using ifconfig has no effect on the priority of the card being chosen as Linux uses the Metric value in its routing table to decide the priority.
- RX Packets, TX Packets - The next two lines show the total number of packets received and transmitted respectively. As you can see in the output, the total errors are 0, no packets are dropped and there are no overruns. If you find the errors or dropped value greater than zero, then it could mean that the ethernet device is failing or there is some congestion in your network.
- collisions - The value of this field should ideally be 0. If it has a value greater than 0, it could mean that the packets are colliding while traversing your network - a sure sign of network congestion.
- txqueuelen - This denotes the length of the transmit queue of the device. You usually set it to smaller values for slower devices with a high latency such as modem links and ISDN.
- RX Bytes, TX Bytes - These indicate the total amount of data that has passed through the ethernet interface either way. Taking the above example, I can fairly assume that I have used up 31.6 MB in downloading and 2.5 MB uploading which is a total of 37.1 MB of bandwidth. As long as there is some network traffic being generated via the ethernet device, both the RX and TX bytes will go on increasing.
- Interrupt - From the data, I come to know that my network interface card is using the interrupt number 9. This is usually set by the system.
Learning to use the right command is only a minuscule part of the job of a network administrator. The major part of the job is in analyzing the data returned by the command and arriving at the right conclusions.
Labels: howtos, system administration
LinuxBIOS - A truly GPLed Free Software BIOS
 A few months back, I had posted an article related to BIOS which described its functions. A BIOS is an acronym for Basic Input Output System and is the starting point of the boot process in your computer. But one of the disadvantages of the proprietary BIOS which are embedded in most PCs is that there is a good amount of code which is used in it to support legacy operating systems such as DOS and the end result is a longer time taken to boot up and pass the control to the resident operating system.
A few months back, I had posted an article related to BIOS which described its functions. A BIOS is an acronym for Basic Input Output System and is the starting point of the boot process in your computer. But one of the disadvantages of the proprietary BIOS which are embedded in most PCs is that there is a good amount of code which is used in it to support legacy operating systems such as DOS and the end result is a longer time taken to boot up and pass the control to the resident operating system.- 100% Free Software BIOS (GPL)
- No royalties or license fees!
- Fast boot times (3 seconds from power-on to Linux console)
- Avoids the need for a slow, buggy, proprietary BIOS
- Runs in 32-Bit protected mode almost from the start
- Written in C, contains virtually no assembly code
- Supports a wide variety of hardware and payloads
- Further features: netboot, serial console, remote flashing, ...
Is Free Software the future of India? Steve Ballmer CEO of Microsoft answers...
Labels: slashdotted
Book Review: Ubuntu Hacks
 I recently got hold of a very nice book on Ubuntu called Ubuntu Hacks co-authored by three authors - Kyle Rankin, Jonathan Oxer and Bill Childers. This is the latest of the hack series of books published by O'Reilly. They have made available a rough cut version of the book online ahead of schedule which was how I got hold of the book but as of now you can also buy the book in print. Put in a nutshell, this book is a collection of around 100 tips and tricks which the authors choose to call hacks, which explain how to accomplish various tasks in Ubuntu Linux. The so called hacks range from down right ordinary to the other end of the spectrum of doing specialised things.
I recently got hold of a very nice book on Ubuntu called Ubuntu Hacks co-authored by three authors - Kyle Rankin, Jonathan Oxer and Bill Childers. This is the latest of the hack series of books published by O'Reilly. They have made available a rough cut version of the book online ahead of schedule which was how I got hold of the book but as of now you can also buy the book in print. Put in a nutshell, this book is a collection of around 100 tips and tricks which the authors choose to call hacks, which explain how to accomplish various tasks in Ubuntu Linux. The so called hacks range from down right ordinary to the other end of the spectrum of doing specialised things.Book Specifications
Name : Ubuntu Hacks
Authors : Kyle Rankin, Jonathan Oxer and Bill Childers
ISBN No: 0-596-52720-9
No of pages: 447
Price : Check at Amazon.com or compare prices of the book.
Rating: Very good
Labels: book reviews, ubuntu
A list of Ubuntu/Kubuntu repositories
Labels: repositories, ubuntu
Learning to use netcat - The TCP/IP swiss army knife
For the server :
nc -l <port number >nc <server ip address> <port number>- You can transfer files by this method between remote machines.
- You can serve a file on a particular port on a machine and multiple remote machines can connect to that port and access the file.
- Create a partition image and send it to the remote machine on the fly.
- Compress critical files on the server machine and then have them pulled by a remote machine.
- And you can do all this securely using a combination of netcat and SSH.
- It can be used as a port scanner too by use of the -z option.
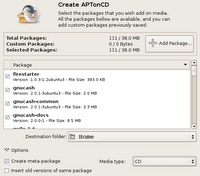
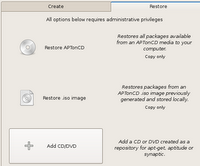
AptonCD - Create a backup of all the packages you have installed using apt-get
On Ubuntu for instance, you can install it using the command:
# sudo apt-get install aptoncdSo how do you use the program ?
- Restore all packages available from an AptonCD media (read it as CD or DVD) on to the computer.
- Restore packages from an AptonCD ISO image previously generated and stored locally.
- Add a CD/DVD created as a repository for apt-get, aptitude or synaptic. Which means the program adds the necessary lines of code required in the /etc/apt/sources.list file which will enable you to use apt-get or any similar program to install the software on the CD.
A talk with Jon Maddog Hall - the spokesman for the open source community and president of Linux International
 Jon Hall, president of Linux® International, is a passionate spokesman for the open source community and ideal. Over a 30-plus-year career, Hall has been a programmer, systems designer, systems administrator, product manager, technical marketing manager, author, consultant to local, state and national governments worldwide and college educator. He is currently an industry consultant. While at Digital, he became interested in Linux and was instrumental in obtaining equipment and resources for Linus Torvalds to accomplish his first port, to Digital's Alpha platform. Hall serves on the boards of several companies, and several nonprofit organizations. At the U.K. Linux and Open Source Awards 2006, he was honored with a Lifetime Recognition Award for his services to the open source community.
Jon Hall, president of Linux® International, is a passionate spokesman for the open source community and ideal. Over a 30-plus-year career, Hall has been a programmer, systems designer, systems administrator, product manager, technical marketing manager, author, consultant to local, state and national governments worldwide and college educator. He is currently an industry consultant. While at Digital, he became interested in Linux and was instrumental in obtaining equipment and resources for Linus Torvalds to accomplish his first port, to Digital's Alpha platform. Hall serves on the boards of several companies, and several nonprofit organizations. At the U.K. Linux and Open Source Awards 2006, he was honored with a Lifetime Recognition Award for his services to the open source community.
Labels: interviews
Drupal 5.0 beta scaling new heights in the Content Management Systems arena
It is now easier to navigate across different settings in the administer section as it is now broadly divided into 5 intuitive sections them being Content Management, Site Building, Site Management, User Management and Logs. Again the contents in the administer section can be sorted by task or by modules.